A grounding framework builds a shared comprehensive understanding which enables meaningful and insighful discussions.
From Data to Action Story
Data aggregated and placed in a context to create information. That information can then be applied to intended use cases to deliver insight. Finally, those insights are leveraged to help transform operations through optimized decision-making and automated actions.
Digital Engineering: Engineering the Transformation
Digital Engineering is a cultural shift, changing the way people think about their systems, systems of systems, and how they make changes. It allows organizations to take a more dynamic approach to design decisions by providing a method for testing changes rapidly rather than the current static process which often forces engineers to investigate potentially thousands of pages of documentation. This allows organizations to explore a larger trade space at any point in a system’s lifecycle greatly reducing resources spent on document exploration and editing to allow more focus on analysis.1
Digital Engineering enables the true Digital Transformation of organizations using Industry 4.0 technologies. Digital Engineering (DE) develops digital artifacts which support creating and sustaining a complex system during its lifecycle. Engineering comes from the latin root gene which means to create, invent or bring forth, manufacture or produce. From a product and production perspective, the product artifact is the Digital Twin and the production line artifact is the Digital Thread.
Digital Twin
A Digital Twin is a digital representation of the complex system and its lifecycle. It is the the Authoritative Source of Truth (ASoT) which support the alignment of connected workstreams. It is a software product. Software Products fall into two broad categories. Generic products are stand-alone systems that are developed by a production unit and sold on the open market. Customized Products are the systems that are commissioned by a particular customer. Digital Twin is a customized software product commissioned by the owner.
Digital Thread
A Digital Thread serves as the foundational framework that enables the creation and operation of Digital Twins. It connects data and information throughout a product's lifecycle to ensure continuity and traceability of data. As Software products are produced with the help of the software process. The Digital Thread is is a way in which we produce a Digital Twin. Digital Thread is a software process.
Levels of Abstraction (LoA): Cloud to Ground Perspectives
"Good programmers are relentlessly curious about how things work, not just at the level of code but at all levels of abstraction." Andrew Hunt and David Thomas
A level of abstraction (LoA) is a finite but non-empty set of observables (concpets). By identifying the LoA we could think of technologies in term of decoupled layers. Each LoA sets a kind of boundaries where a group of concpet could be used with specific semantics. It is important to identify at which level a question belongs for more oriented discussion.
For example: The following senctence could be discussed in more insightfull manner if we could identify a specific LoA. The focus on triangular meshes as the main geometric representation offers advantages in terms of performance and compatibility, but raises questions about how to preserve design intent and parametric information.
Data LoAs
| LoA | Type | Purpose | Model | Representation | Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disk | data, metadata | Persistent Layer, Storage Layer, Archieving Layer, Cold Layer | Data Model | files, folders, tables | seralizers, db Engines, filesystem |
| Memory | data, metadata | Hot layer | Data Model | data structures (array, tree, list , graph) | parsers, loaders |
| Memory | semantics | Processing layer, Runtime Layer | Information Model | ontologies, schema, standards | runtimes, application processes, APIs |
| Network | packets | Sync layer | Protocols | memory buffers | seralizers |
examples
- Data is assets on Disks.
- Single source of truth, Documentation, Versions (Time)
- data consistency: data accuracy, completeness, and correctness.
- Data is a live in-memory.
- interoperability: data exchange across systems
- semantics: Standardize understanding of data across systems/domains
- if there is no need to interpret the content of a file; it could be simply treat it as a sequence of bytes.
- In network programming, data usually resides in memory buffers, and you can transmit those bytes over a network using system calls or higher-level APIs.
- What is important is the ability to identify the smallest meaningful change to sync (diff)
Insights
- A Data Model has two different representations.
- seralizers have two different implementations.
Data Value LoAs
More and more information is transmitted every day, and a significant part of this information is expressed in the form of data. Unlike images or language, this data is not transparent to most of us. However, it is necessary to fuel the services, automations and AI available to us.
The terms, Data, information, and knowledge represent different stages of value creation. Data in their simplest form consist of raw alphanumeric values.
Information is created when data are processed, organized, or structured to provide context and meaning. Knowledge is unique to each individual and is the accumulation of past experience and insight that shapes the lens by which we interpret, and assign meaning to, information. Data is meangingless until it is processed, and actionless until contextualized with a purpose.
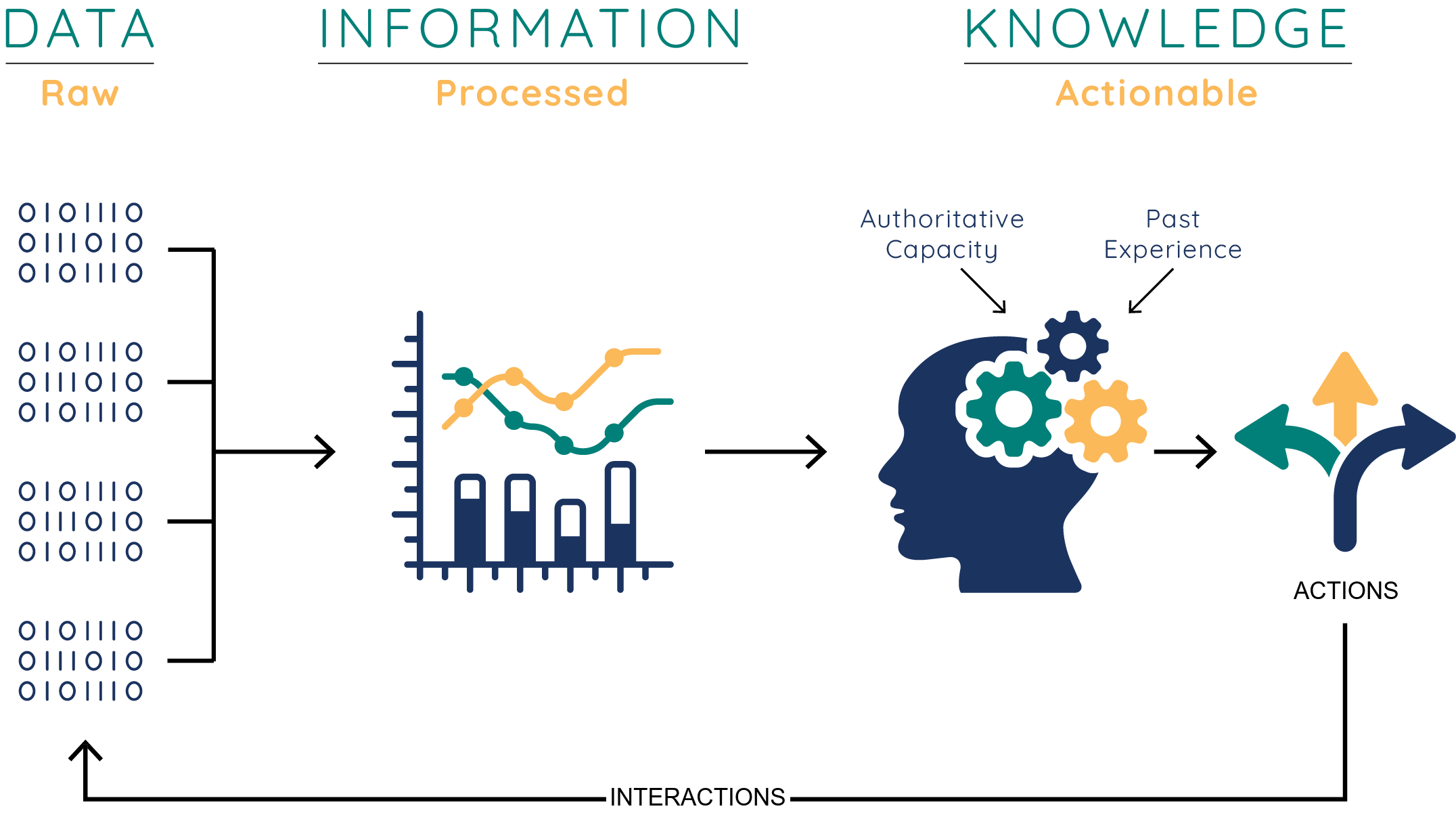
The flow from data to information and knowledge is not uni-directional. The knowledge gained may reveal redundancies or gaps in the data collected.
| LoA | Nature | Meaning | Processing | Quantifiability | Overload Possibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data | Is objective | Has no meaning (raw facts) | Is unprocessed | Is quantifiable | There can be data overload |
| Information | Should be objective | Has meaning (structured data) | Is processed | Is quantifiable | There can be information overload |
| Knowledge | Is subjective | Has meaning for a specific purpose | Is processed and understood | Is not quantifiable | There is no knowledge overload |
| Decision | Data-driven | Leads to choices & conclusions | Involves reasoning & evaluation | Partially quantifiable | There can be decision fatigue |
| Action | Behavior, Cognitive | Translates decisions into outcomes | Execution of a chosen strategy | Not quantifiable | There can be action overload |
| Interaction | Feedback, Learning Loop | Generates new data & insights | Iterative adaptation & refinement | Not quantifiable | Can lead to feedback fatigue |
Human Data Interaction (HDI)
Cognitive Behavioral (CBT) suggests that our thoughts and behavior are all connected. CBT is often misrepresented as being concerned with ‘fixing’ faulty thought processes. CBT is fundamentally about the meanings which people make of their experiences.

Human-data interactions improve the way we understand and use the information contained in data. HDI is about how people interacts with data and how they interact with other people through data intensive systems. According to (Kymmell, 2008)2, these actions and interactions could be categorized as visualization, understanding, communication, and collaboration.
Through multiple interactions we will dramatically change the way we visualize and understand our environment (cognition). Hence, change the the way we communicate and collaborate with others and ourselves (behaviours).
A: [
C: circle rad 100% invisible;
COL: circle rad 50% at 1.0 n of C.n thickness 150% fill Navy;
TCOL: text "Collaboration" at 0.25 n of COL;
COM: circle rad 50% at 1.0 e of C fill Crimson;
TCOM: text "Communication" ljust at 0.25 s of COM;
VIS: circle rad 50% at 1.0 s of C fill DarkMagenta;
TVIS: text "Visualisation" at 0.25 s of VIS;
UND: circle rad 50% at 1.0 w of C fill Teal;
TUND: text "Understanding" rjust at 0.25 n of UND;
line from VIS.c to COM.c to UND.c close invisible;
line from VIS.c to COL.c to UND.c close invisible;
line from COL.c to COM.c to UND.c close invisible;
;
line from COL.s to VIS.n thickness 150%;
line from COL.sw to UND.ne thickness 150%;
line from COL.se to COM.nw thickness 150%;
;
line from VIS.nw to UND.se thickness 150%;
line from VIS.ne to COM.sw thickness 150%;
line from UND.e to COM.w dashed color gray thickness 150%;
]
Caption: text "Agents Actions and Interactions Categories" italic with .n at 0.1in below A.s;
→ /pikchrshowThe figure shows the connectivity among the concpets and how both generate and reinforce one another. For instance, an alternative routes to gain collaboration can be approached through visualization, communication, or understanding. With the rise of Agentic Systems and LLM, the agent term refers to both human and AI agents.
Summary
A system of systems framework can provide essential supporting structures that enable collaborative environments for all stakeholders, practitioners, and decision makers, engaging all parties to facilitate decision making from distributed locations.
Additionally, the human-centered nature of Digital Engineering can reduce the gap in understanding the subject matter, allowing for efficient and rigorous analyses driven from data. The increased collaboration capability allows for iterative, yet concurrent execution of verification and validation throughout the project lifecycle, which can reduce ambiguity and the project timeline.
- ^ Deloitte Consulting. (2022). Managing your Organization’s Complexity Through Digital Engineering. Deloitte Consulting LLP.
- ^ Kymmell, W. (2008). Building information modeling: Planning and managing construction projects with 4D CAD and simulations. McGraw-Hill.:w